
Essential WordPress Security Tips for Site Owners! WordPress is one of the most popular website platforms worldwide. Millions of websites use it. But with popularity comes risk. Hackers often target WordPress sites.
To keep your website safe, you must take precautions. Protect your content and data by following Essential WordPress Security Tips. This will reduce the chances of cyber attacks and help your site run smoothly.
In this article, we’ll cover Essential WordPress Security Tips for Website Owners. We’ll talk about updating your WordPress version and plugins, using strong passwords, and adding security plugins.
These steps will help you strengthen your website’s security and block unauthorized access. By following these tips, you can keep your website safe and protect your online presence.
Why are WordPress sites hacked?

WordPress is one of the most popular content management systems, powering about 35% of all websites. Its ease of use, flexibility, and a vast range of plugins and themes make it a top choice for creating websites and blogs quickly. As a result, its popularity is the main target for hackers.
One main reason WordPress sites are often hacked is their widespread use. With millions of sites using WordPress, hackers have many potential targets, making WordPress more attractive than less common platforms.
Another reason is vulnerabilities in WordPress core, plugins, and themes. While WordPress is generally secure, outdated versions of the platform, plugins, or themes can have security flaws that hackers exploit. Poorly coded plugins or themes can also create weak points that invite attacks.
The many plugins and themes in WordPress are both an advantage and a potential risk. While they add customization and functionality, some plugins might be poorly coded or even malicious. Using pirated or nulled themes and plugins can also expose your site to hacking.
Weak passwords and poor security practices are additional risks. Simple, easy-to-guess passwords, not updating WordPress regularly, and not using security measures like firewalls or security plugins increase the chance of getting hacked.
WordPress sites are frequently hacked due to their popularity, potential vulnerabilities, and weak security practices. Website owners must understand these risks and take proactive steps to secure their sites against hacking attempts.
Essential WordPress Security Tips
You can do many things to keep your website secure, like updating plugins and backing up your site. You can also consider more advanced options, like switching to a host with better security.
Here are some tips for Site Owners to maintain a safe and functional website:
1. Regular Updates
- Keep Your WordPress Core Updated: Keep Your WordPress Core Updated: Make sure your WordPress core is always up to date. Keeping WordPress updated ensures your site stays secure and runs smoothly. Updates fix vulnerabilities and improve performance. Always stay current to protect your website. Regular updates protect against vulnerabilities and improve performance.
- Plugins and Themes: Regularly update all plugins and themes to fix security issues.
2. Security Plugins
- Install trusted security plugins like WPScan or Admintosh to protect against malware and other threats. So, you use the best plugin for WordPress security. Admintosh is the best free WordPress security plugin where you will get many essential features to prevent security threats.
3. Use Strong Passwords
- Ensure all user accounts, especially admin ones, have strong, unique passwords.

4. Regular Backups
- Always back up your website’s data regularly. Use plugins like UpdraftPlus to automate backups. Always back up your website’s data regularly. Use plugins like UpdraftPlus to automate backups. Regular backups ensure you have a copy of your site if something goes wrong.
5. Monitor Website Health
- Use free tools like Google Safe Browsing, Sucuri SiteCheck, or VirusTotal to scan for malware and vulnerabilities.
6. Limit Login Attempts
- Limit Login Attempts Helps stop hackers from guessing your password using automated tools. Set up a lockout system to block repeated failed login attempts. After a certain number of failed tries, the user gets locked out temporarily. This helps protect your site from unauthorized access and brute-force attacks.
7. Use HTTPS
- HTTPS is vital for WordPress security because it encrypts data between your website and visitors’ browsers. This protects sensitive information like login credentials, personal details, and payment data from hackers. Without HTTPS, this information is sent in plain text, making it easy for attackers to steal.
- Another key benefit of HTTPS is authentication. It ensures that visitors are connected to the legitimate, secure version of your website. This helps prevent phishing attacks, where hackers create fake sites to trick users into giving away sensitive information.
- HTTPS also boosts your website’s search engine ranking. Since 2014, Google has used HTTPS as a ranking signal, meaning sites with HTTPS are more likely to rank higher in search results.
8. Use Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
- Two-factor authentication adds extra security. With 2FA, users need to provide a second verification form, like a code sent to their phone or email, and their password. This makes it much harder for hackers to get in, even if they guess the password.
- 2FA greatly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. If a hacker steals your password, they need a second code. This extra step provides strong protection for your site.
- Setting up 2FA is simple. Many WordPress plugins can help you enable this feature with just a few clicks. No advanced technical skills are needed.
9. Regularly scan for malware
- Use a third-party tool or security plugin to scan your website for malware. This software checks your site’s files, plugins, and themes for any infections. If it finds a problem, it will show you where it is.
- Remember how antivirus scans on your computer used to take a long time? Now, most antivirus software runs in the background and alerts you only if there’s an issue. Jetpack Security also handles malware scans effectively.
- Unlike other tools that just tell you there’s a problem, Jetpack usually offers solutions, often with a single click.
- If you secure your site well, malware infections should be very rare. Still, it’s good to have automatic malware scans set up in case of unexpected attacks.
10. Disable file editing in your wp‑config.php file
- WordPress lets you edit files directly from the dashboard using plugin and theme file editors.
- These editors allow you to change your site’s code without using FTP. However, if a hacker gets access to an account with editing permissions, they can cause serious damage.
- To prevent this, you may want to disable file editing in WordPress. You can do this by adding a line of code to the wp-config.php file.

[Some themes and plugins automatically disable file editing. If you don’t see the editors in the dashboard, your theme or plugin might have already turned this feature off.]
11. Hide your wp‑admin login URL
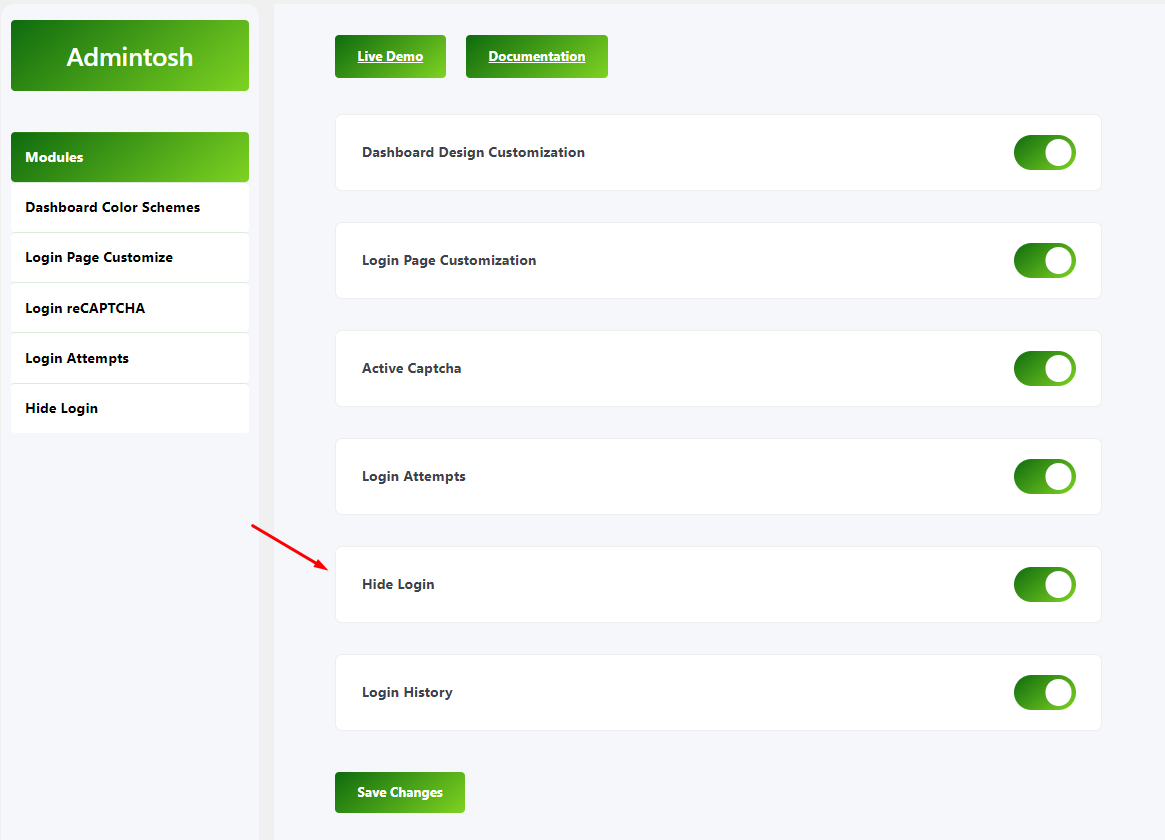
- One way to protect your WordPress admin is by changing the URL of your login page. Combined with extra password protection, this makes it very hard for attackers to access your dashboard.
- You can manually change the wp-login URL, but using a plugin makes it easier. Admintosh is a simple plugin that lets you set a new login URL without touching your site’s code.
- After installing the plugin, go to Settings → Admintosh. Find the option that says “Hide Login.” Then, replace the default URL with a custom one.
- Pick a random mix of letters and numbers to make it tough for attackers to guess. Just remember to bookmark the new login page or choose a URL you can easily recall.
12. Change the default WordPress database prefix
Every WordPress database has a name, usually starting with “wp_”. This prefix allows attackers to easily guess your database name.
Changing the prefix can make it harder for attackers, but it’s not an easy task. You’ll need to edit core files and make changes to the database, so be sure to back up your site first.
To start, access your site via FTP and open the wp-config.php file. Find the line with the prefix and replace “wp_” with something unique, like “newprefix_”. Save the file.

Next, go to your database using phpMyAdmin. Choose your WordPress database, then click on “SQL” at the top. Here, you’ll update the table prefixes to match your new one.
Default tables include:
- wp_options
- wp_posts
- wp_comments
You’ll need to run an SQL command for each table to change the prefix. Remember, some plugins add their own tables, so update those as well.
After changing the prefixes, go back to your WordPress dashboard. Deactivate and reactivate all plugins and themes, as they won’t recognize the updated database until you do this.
Finally, check your site to ensure everything is working properly.
13. Keep your PHP version up‑to‑date
- WordPress relies heavily on PHP, a programming language that handles most admin tasks.
- PHP is software that gets regular updates with new features, better performance, and security improvements. WordPress needs your server to run PHP version 7.4 or higher. Newer versions offer even better performance and security, which benefit WordPress too.
- Most good web hosts update PHP automatically as new versions are released. Some hosts let you switch between PHP versions manually, which can help fix errors on your site.
- To check your PHP version, go to your WordPress dashboard and navigate to Settings → Site Health → Info → Server. You’ll see your server’s details, including the PHP version.
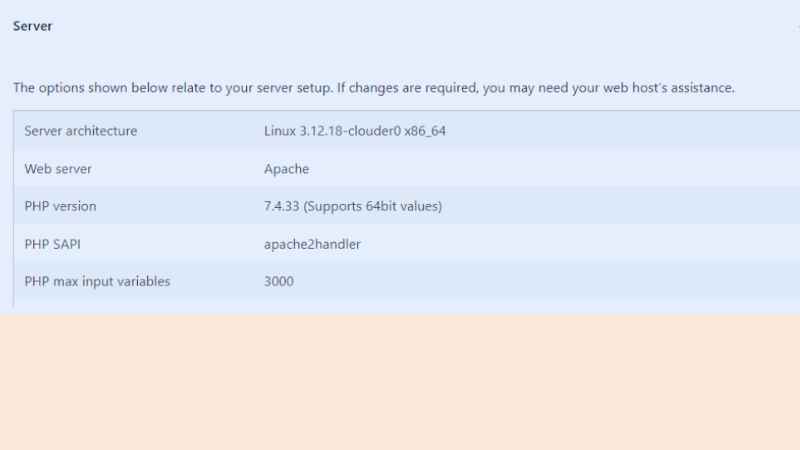
- If the version is outdated, contact your web host to update it. However, with a reliable hosting provider, they should handle this for you.
14. Turn off PHP error reporting
- WordPress includes a debugging tool that logs PHP errors. You can use these logs to fix technical issues on your website.
- However, these error logs can create security risks. If attackers access them, they could learn about your site’s plugins and important files.
- You don’t need PHP error reporting unless you’re troubleshooting a problem. Once you’ve gathered the information you need, it’s best to disable WordPress debug mode.
- To disable PHP error reporting, edit the wp-config.php file in your WordPress root directory. You can reach this file through FTP.
Open the wp-config.php file and add this code line:

- Change “true” to “false” and save the file. This will turn off error logs in WordPress.
- You can enable them again anytime by changing the value back to “true.”
Practical Health Check Schedule
Weekly:
- Check for and install updates for WordPress core, plugins, and themes.
- Use a security plugin to scan your website for malware. Regular scans help you detect and remove any threats early.
Monthly:
- Review and remove unnecessary or inactive plugins and themes.
- Change passwords for all admin accounts.
Quarterly:
- Perform a full website backup and store it securely.
- Test website functionality to ensure everything is working.
Working with Vendors: Quick Tips for Non-Tech Business Owners
Regular Check-Ins: Schedule regular meetings to discuss system health, updates, and concerns.
Set Update Schedules: Agree on a schedule for regular updates and patches to keep your systems secure.
Periodic Assessments: Arrange for security assessments to identify and fix vulnerabilities.
Backup Plans: Ensure your vendor has a clear backup plan and knows how to handle issues.
Clear Communication: Keep communication open and ensure your vendor understands your needs.
By following these steps, you can keep your website secure and running smoothly without needing to dive into technical details.
conclusion
Keeping your WordPress login safe is key to protecting your website. Follow the WordPress Security Tips shared in this article to strengthen your site and reduce the risk of unauthorized access. Regularly update plugins and themes, use strong passwords, enable two-factor authentication, and limit login attempts. Stay proactive and alert to keep your site secure.